Atyrau region

General information. Atyrau region borders on the Astrakhan region of Russia in the west, and its southern border runs along the coast of the Caspian Sea. Atyrau region is one of the western regions of Kazakhstan. Its area is relatively small - 118.6 thousand km2. This is the 13th place among 20 regions.
Population: As of December 1, 2024, the population of the region was 710.2 thousand people, including urban residents - 390.7 thousand people (55%), rural residents - 319.5 thousand people (45%).
Administrative division. The regional center of the region is the city of Atyrau. There are 2 cities (Atyrau, Kulsary) and 165 villages in the region. The territory of the region consists of the city of Atyrau and 7 rural districts (Inder, Zhylyoi, Isatay, Makat, Makhambet, Kurmangazy, Kyzylkoga).
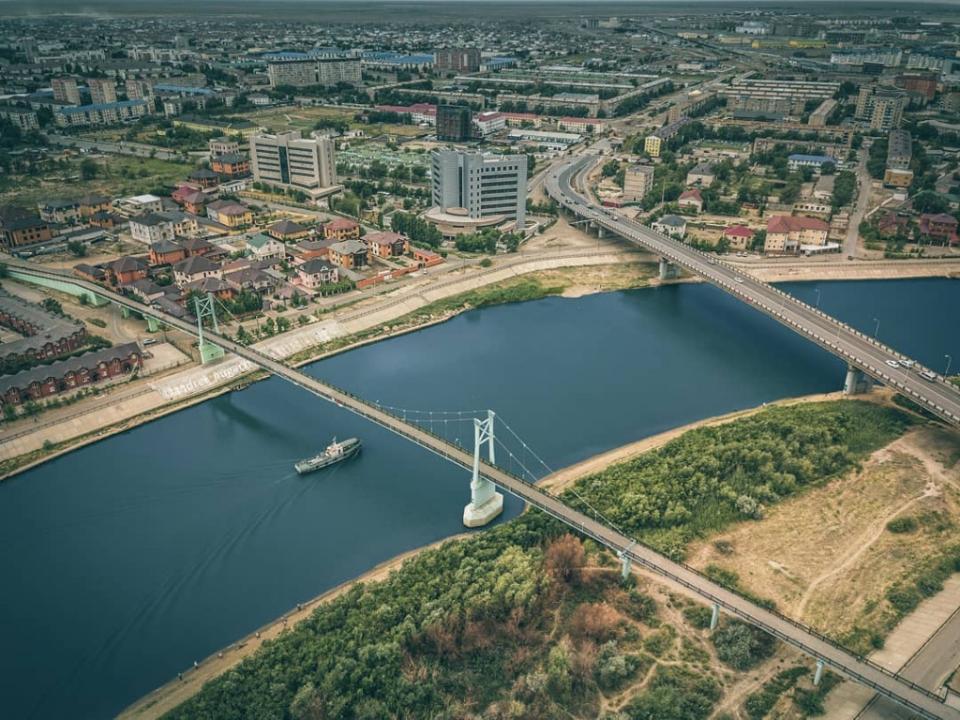
Regional center and history of the region. Often called the "oil capital of Kazakhstan", Atyrau is located in the south of Atyrau region, at the mouth of the Ural River, where it flows into the Caspian Sea.
The history of the city dates back to the 17th century. In 1640, the merchant Gury Nazarov built a wooden settlement here, and later the stone town of Yaitsk appeared here, which was under the control of the Yaitsk Cossack troops (later renamed Lower Yaitsk).
Since the 19th century, the settlement was named after the founder of the settlement, Guryev, and then simply Guryev. The city held this name until 1991. After our country gained independence, the city's Council of People's Deputies changed the name of the city to Atyrau. This word translated from Kazakh means "mouth of the river" or "delta of the river".
In 1938, Guryev region was formed within the Kazakh SSR, with the city of Guryev as its center. At that time, the region occupied a larger territory than it does today. It included the territory of the present-day Mangystau region, a number of Aktobe districts, and bordered the states of Russia, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. After the discovery of the natural resources of Mangystau and the construction of the city of Shevchenko (now Aktau), the territory of the region was divided into Mangystau and Guryev regions. Since October 9, 1991, Guryev region has been renamed Atyrau region.
Natural and climatic conditions. The region is located in the northeastern part of the Caspian Sea basin. It occupies the Zhem Kyrat and the western part of the Ustyurt. Most of the territory is a flat steppe, sloping from north to south. The relief of the northern region is 200 meters above sea level, and in the south it is 20 meters below.
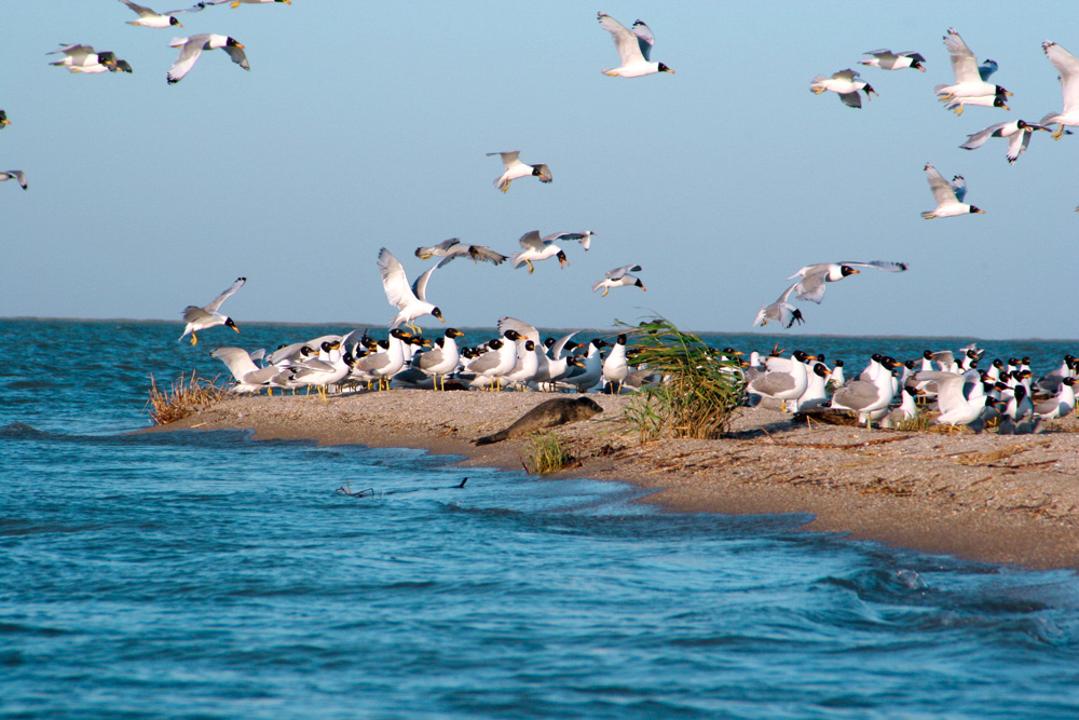
Most of the lands of the Atyrau region are occupied by sand dunes and barkan. In the north of the region, wormwood-shrub vegetation prevails, and in the south, wormwood-shrub vegetation. The Caspian Sea coast is covered with reed thickets, and poplars and willows grow abundantly in river and lake basins. Of the animals, wolves, foxes, lynxes, wild boars, saiga antelopes live here, and of the birds, steppe eagles and ospreys live. Commercial fish such as sturgeon, salmon, and bream are caught in the Caspian Sea and the Ural River.
The region does not have enough fresh water resources. There are few rivers belonging to the Caspian Sea basin. The largest river in the region is the Ural. There are many small lakes in the river valleys and on the Caspian coast that dry up in the summer and turn into salt marshes.
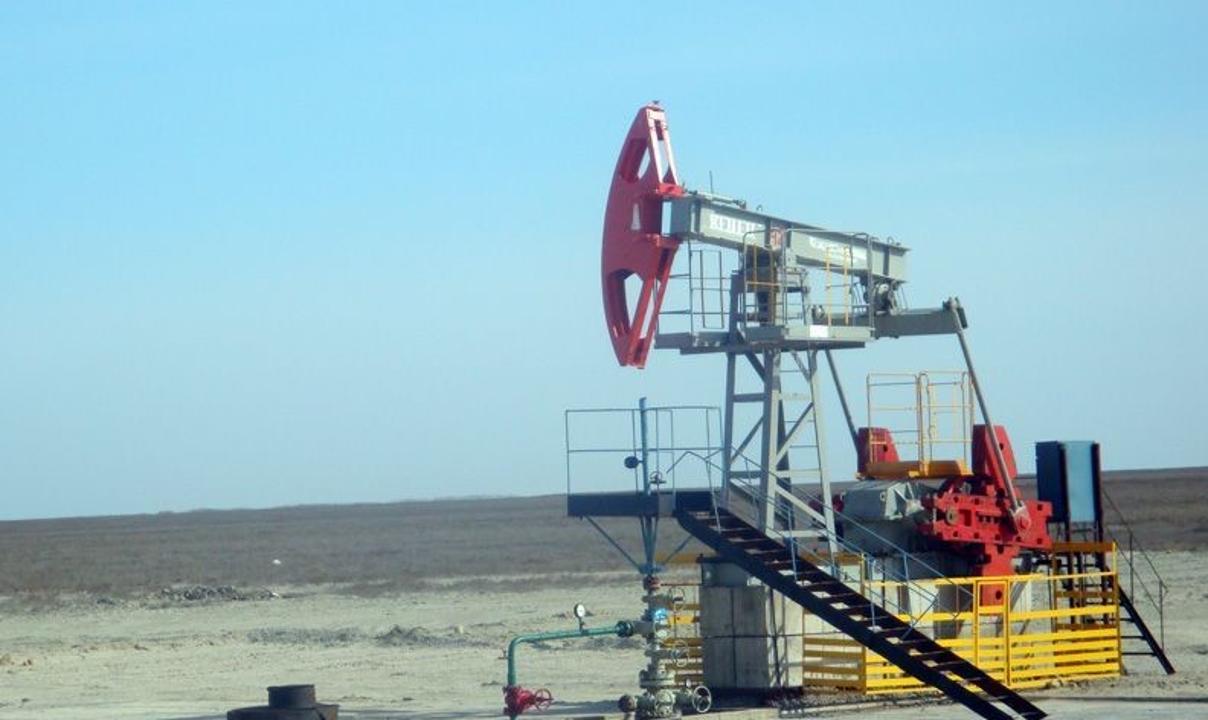
The climate of the region is continental. There is little snow in winter, and summer is dry and hot. The average temperature in January is -3-5 ºС, and the average temperature in July is -24-25 ºС. The subsoil of the Atyrau region is rich in hydrocarbons. Tengiz, Kulsary, Baishonas, Karaarna, Kenbai, etc. There are oil and gas reserves in the fields. There are also deposits of sodium and potassium salts in the region.
Economy. The economy of the region is mostly focused on oil production. In 2022, the volume of industrial output amounted to KZT 13.1 trillion; Atyrau region is the leader by a wide margin of all regions in the country. However, gross agricultural output in 2022 amounted to only KZT 133.4 billion.
The largest enterprises in the region include Atyrau Oil Refinery, Tengizshevroil, Embamunaygas, NCOC.NV, and Atyrau Neftemash.
Engineering, food, and construction industries have also developed alongside the petrochemical industry.
Pipelines Atyrau-Orsk, Uzen-Atyrau-Samara, Atyrau-Novorossiysk all pass through the region.
Tourism. The tourism sector is one of the priority areas of the region's economy. There are opportunities in the region for the development of such types of tourism as historical and cultural (acquaintance with the traditions, history of the region), amateur sports (fishing and hunting), ethnographic and wellness.
Atyrau region occupies a special place in the socio– economic development of Kazakhstan due to its huge economic potential. The number of companies with foreign participation is growing every year. Currently, the region closely cooperates with more than 50 countries around the world. More than 1,000 joint and foreign enterprises have been established and operate in the region.
This cooperation contributes to attracting modern management, real modern technologies, the latest world innovative developments to the field, which ultimately contribute to the development of business tourism and other types of tourism.
The tourist map of the Republic of Kazakhstan includes 6 tourist sites from the Atyrau region at the republican and regional levels. They:
- At the republican level- the complex "medieval Saraishyk" of Atyrau region.
- At the regional level:
- The State Natural Reserve of Atyrau region "Akzhayyk".
- Salt Lake Inder of Atyrau region.
- Naryn sands of Atyrau region.
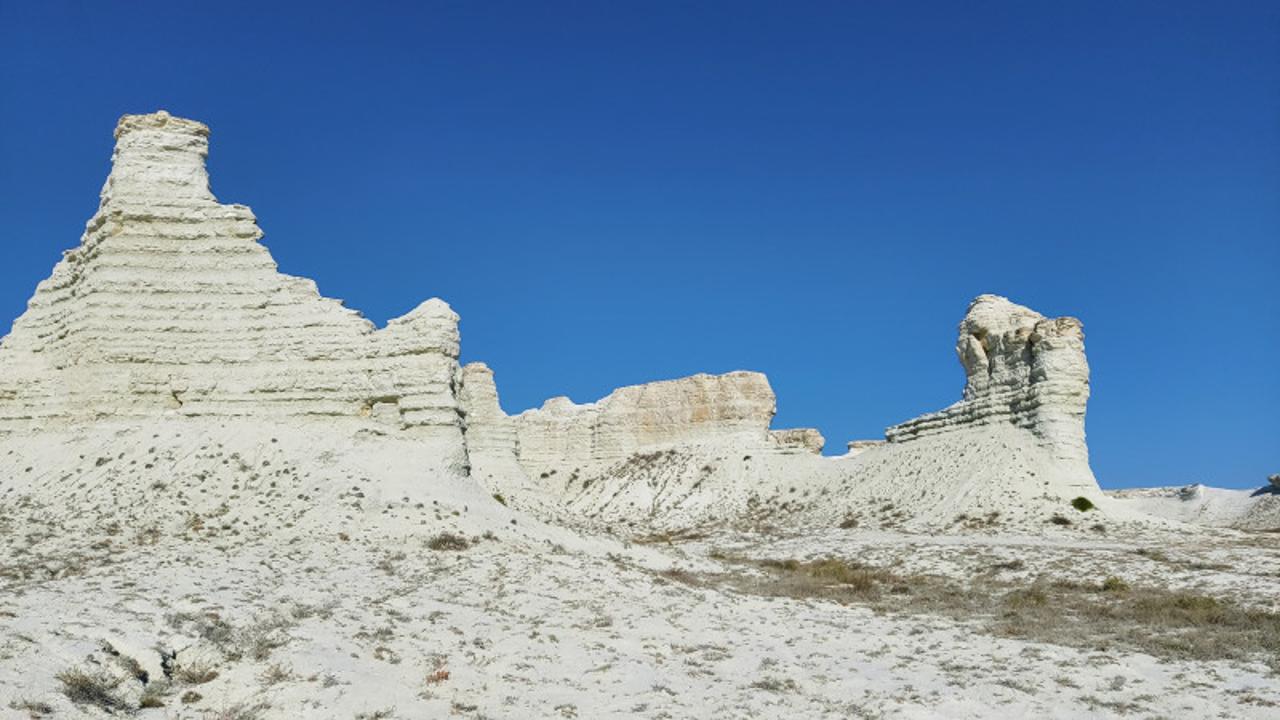
- Chalk mountains "Akkegershin" Atyrau region.
- Lotus fields of Atyrau region.
In addition, there are several tourist sites and recreation sites of historical and cultural significance that are of interest to tourists on the territory of Atyrau region. The most visited by tourists is the Ak Zhaiyk State Nature Reserve. Ecological routes "World of nature" and "World of Water" have been launched in 2 directions on the territory of the reserve. In 12 months of 2022, it has received more than 500 tourists on domestic routes.
Saraishyk town in Makhambet district, one of the most visited places by tourists, Inder salt lake located in Inder district, Naryn Sand in Isatay district, several shrines and cultural monuments in Zhylyoy district. 64 kilometers from the city of Kulsary are the Akmeshit necropolis, Kulshan Ata, the Araltobe necropolis, where "Altyn Adam" was found, the Akkeregeshin mountains, the Imankara cave, the bank of the Kigas River in the Kurmangazy area. Several tourist bases are being built here, and every year in the spring and autumn a large number of Kazakhstani and foreign tourists come to hunt and fish.
A rare lotus flower in the world grows on the territory of Kurmangazinsky district on the Kigas River. The lotus, growing only in natural conditions, creates an unprecedented opportunity for the development of domestic tourism in Kazakhstan.
The number of tourist fishing bases is growing in Kurmangazinsky district. During the season, the influx of tourists coming to rest in the lotus Valley, to tourist fishing bases, has significantly increased. Because a lot of tourists come from the neighboring Astrakhan region to go fishing and have a rest. About 5000 tourists visit the Lotus Valley, tourist bases in seasonal time.
Atyrau region has a number of national historical monuments: for example, the ancient Saraychik fortress, from the period of the Golden Horde. Saraychik is 50 km from Atyrau city and has many exhibits. Famous landmarks include the 19th century Akmeshit Beket underground mosque, and the Artyk mausoleum, a monument to the Kazakh cult-burial architecture of the 19th century.






